Diabetes is a chronic disease of metabolic dysregulation. Insulin in people with diabetes is unable to allow glucose in the blood to enter cells and produce energy for the body, because the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or the insulin produced cannot be used effectively by the body, resulting in a high blood sugar concentration . When the blood sugar level rises above the limit that the kidneys can absorb, the sugar overflows into the urine and is excreted. Because the urine contains sugar, it is called diabetes.
Pre-diabetes
People with impaired fasting blood sugar or impaired glucose tolerance have higher blood sugar levels than normal, but they do not reach the target of diabetes. According to specialists, about 5% to 10% of people with abnormal glucose tolerance will be converted into diabetic patients every year. They are not only a high-risk group of diabetes, but also have a higher chance of suffering from cardiovascular disease. Therefore, these people need to control their diet early and establish a healthy lifestyle.
Risk factors for diabetes
Although diabetes cannot be cured, it is a manageable long-term disease. The cause of the disease has not yet been fully determined, and the following risk factors will increase the chance of suffering from the disease, including “unchangeable” and “changeable” risk factors. Patients should pay more attention to the changeable risk factors and start from the daily routine. To be adjusted in the life style of the country.

Symptoms of diabetes
About half of the patients have no obvious symptoms. If they are at high risk, please have regular checkups and follow-up

Complications of diabetes
Acute complications mainly include hypoglycemic coma and hyperglycemia coma.
The main symptoms of hypoglycemic coma include cold sweats, headache, rapid heartbeat, severe hunger, shaking, very tired, and anxiety.
The main symptoms of hyperglycemia coma include extreme thirst, nausea, vomiting, facial flushing, blurred vision, and fast and deep breathing.
If the treatment is delayed, both can lead to coma and even death.
Chronic complications include:
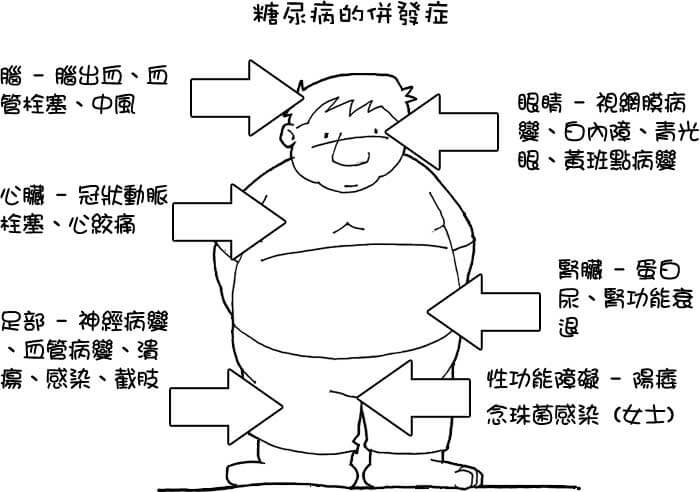
Source:康程式e2care

